This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively utilize markers during the scanning process.

Markers, also referred to as reference points, play a crucial role in 3D scanning. When the scanner operates, it determines the coordinate information by identifying the circular reflective area of the marker, thereby achieving precise spatial positioning. Generally, when utilizing the blue laser mode or infrared marker stitching mode, it is essential to adhere markers to the surface or surroundings of the scanned object prior to commencing the scan.

Markers come in various sizes, specifications, and materials, including options with adhesive backing and magnetic attachment. It is advisable to select the appropriate markers based on the structural dimensions and characteristics of the workpiece. Commonly used handheld markers typically have inner diameters of 6 mm and 3 mm, which can be mixed for optimal results.

Precautions:
Marker Placement Spacing:
To ensure a smooth and complete scanning process, each adjacent frame of data must share at least four common points during continuous stitching. The specific spacing should be determined according to the scanner's size. For example, when using the Raptor X cross-line mode, the recommended spacing for markers is between 60 mm and 100 mm. In contrast, when employing the seven-line parallel mode, the spacing should be between 20 mm and 50 mm.
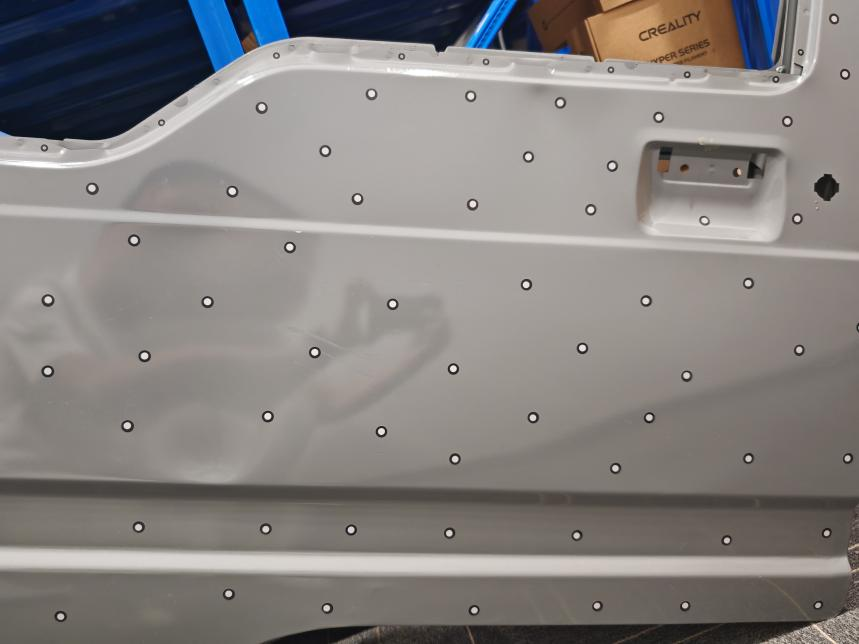

Irregular Distribution:
Markers should be placed in an irregular distribution pattern. Avoid arranging them in regular formations such as straight lines, triangles, or circles. Regularly arranged points can lead to splicing errors, as they may create multiple points of consistency, causing the scanner to misinterpret the data.
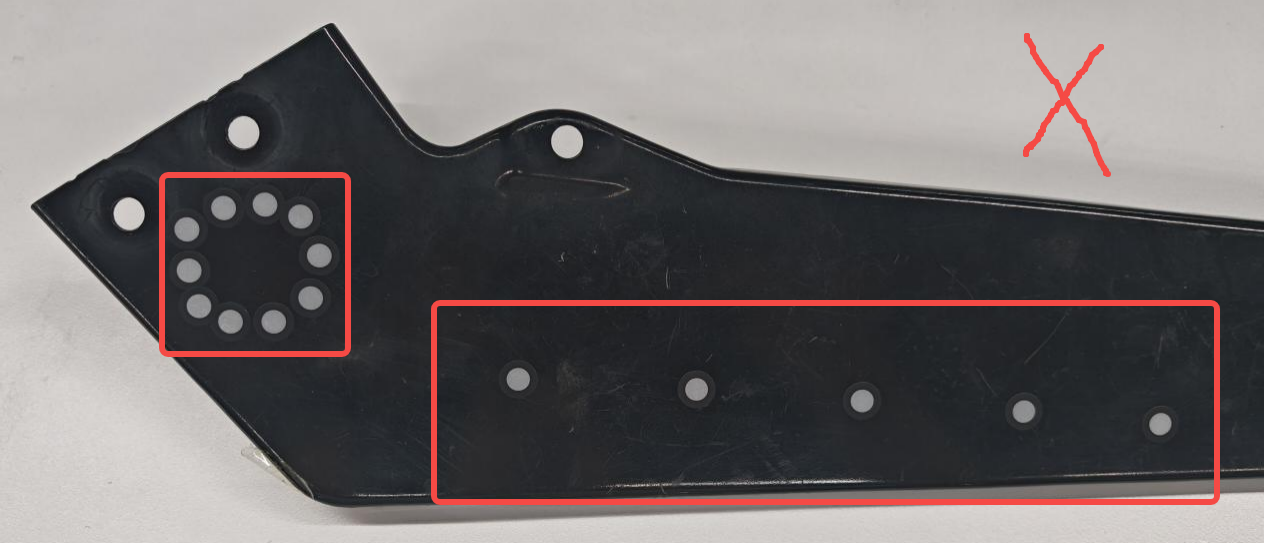

Avoid Special Position:
Markers should be adhered to flat or large curved surfaces to prevent excessive bending after application. Avoid placing markers over features on the workpiece, such as holes or engravings, as this may obscure these details and hinder the scanning process. Additionally, markers should not be applied at right angles or on edges, as this can result in bulges or depressions in the marked areas.
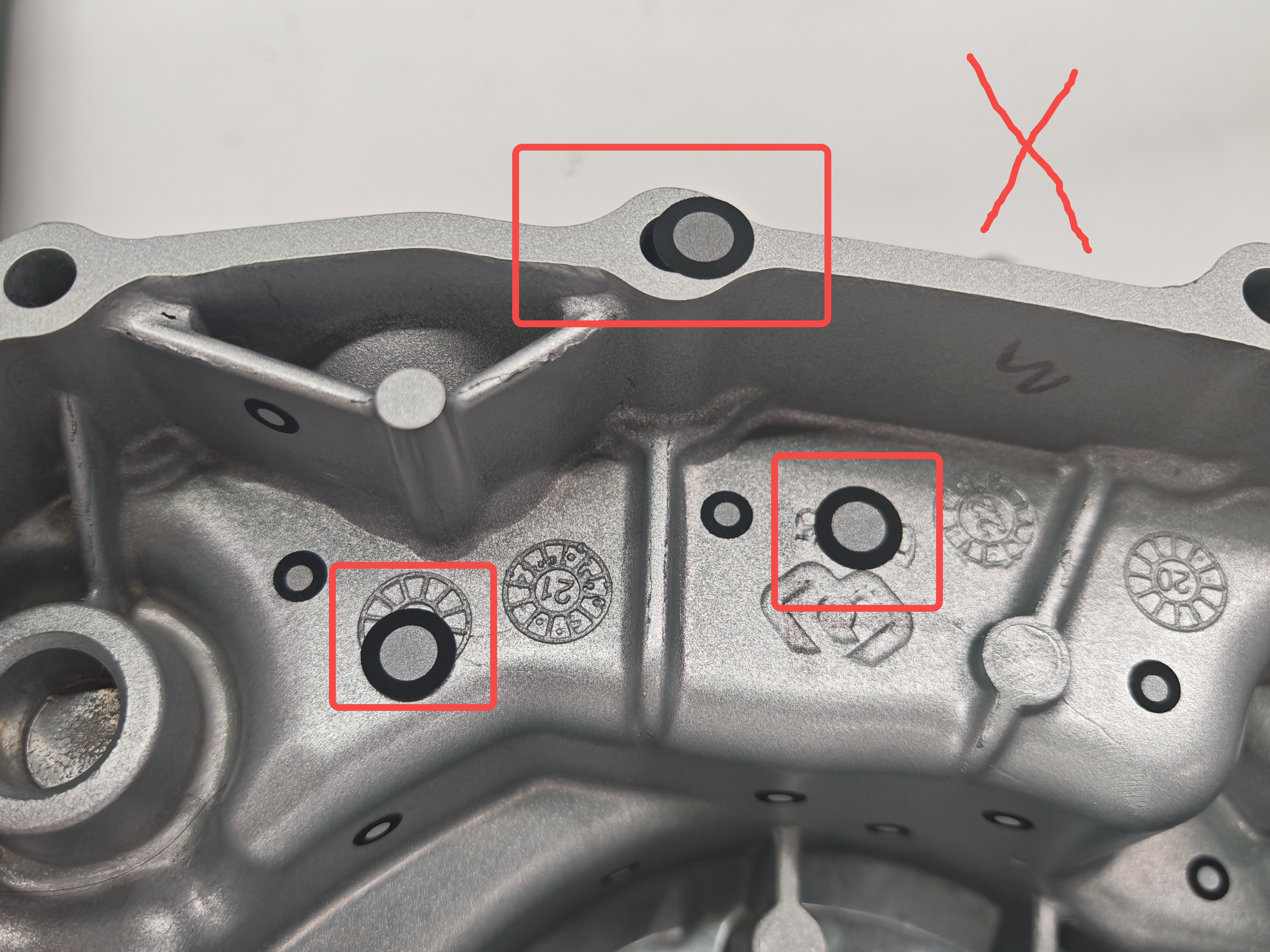
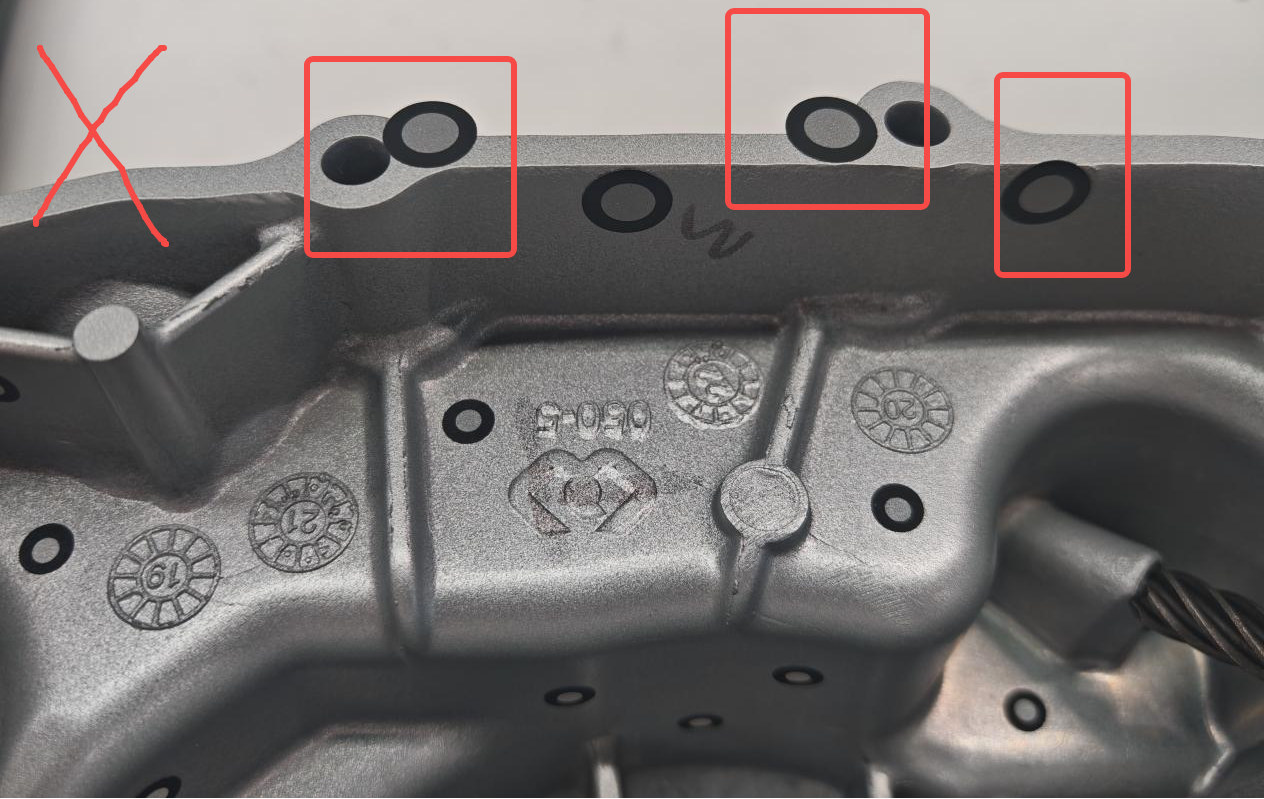
Avoid Damage:
Do not squeeze, rub, or fold the markers, as this may compromise their integrity and effectiveness.